Class I phosphoinositide3-‐kinases in immunity…
93
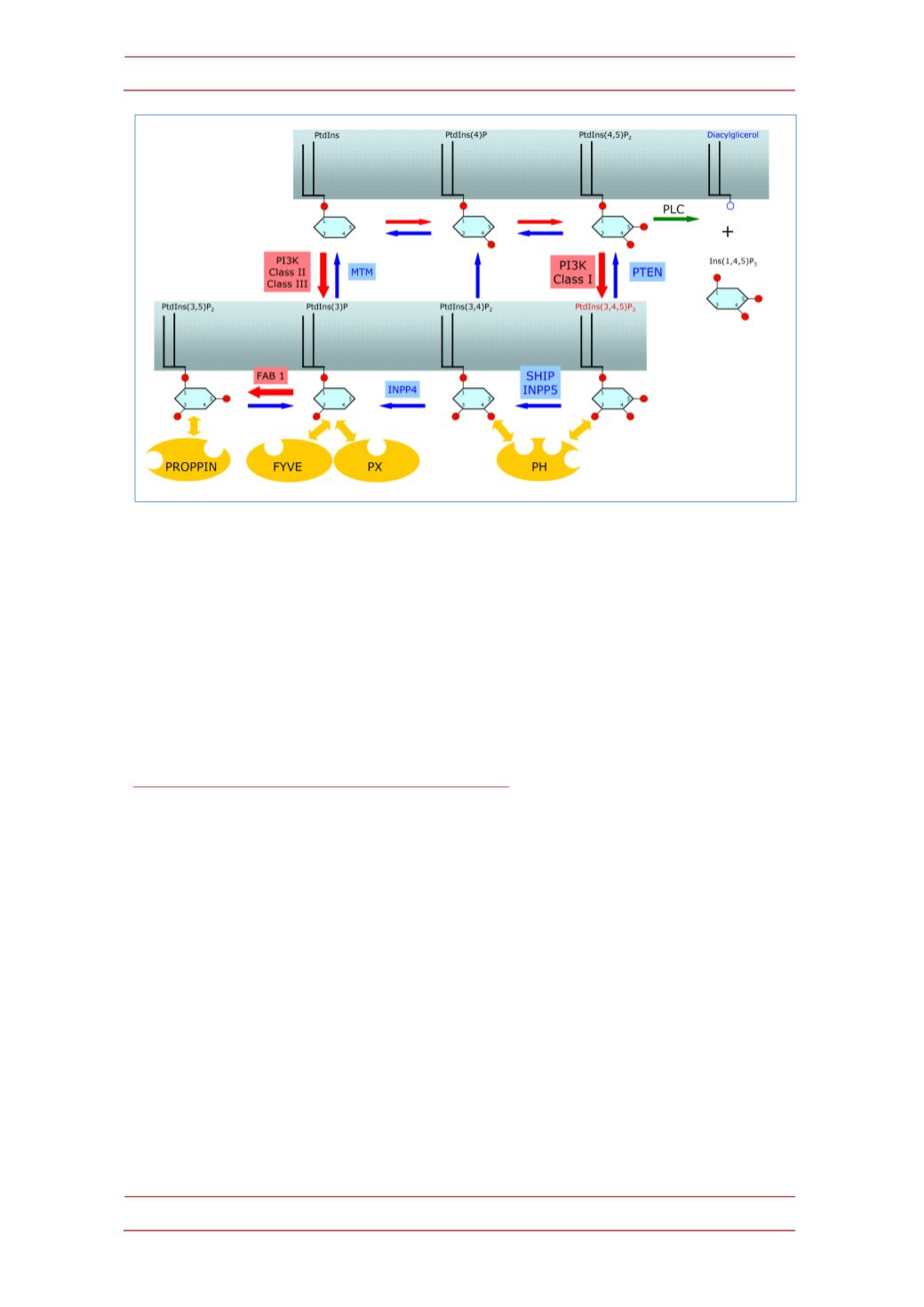
Figure 1.-‐
A summary of phosphoinositide phosphorylation/dephosphorylation steps in the cell
membrane is shown. These phosphoinositides recruit proteins endowed with phosphorylated
inositol lipid-‐binding protein domains that serve to cell signaling. Phosphorylation and
dephosphorylation steps are indicated by red and blue arrows, respectively; steps where PI3K
kinases intervene are shadowed in red; Inositol phosphate phosphatases are shadowed in blue;
effector protein domains binding to different phosphorylated inositol lipids are in yellow.
Abbreviations: FAB1: PtdIns(3)P 5-‐kinase; FYVE: Fab 1 YOTB Vac 1 and EEA1 domain; INPP4:
Inositol polyphosphate 4-‐phosphatase; INPP5: Inositol polyphosphate 5-‐phosphatase; MTM:
Myotubularin; PH: Plecstrin homology domain; PI3K: Phosphoinositide-‐3 kinase; PLC:
Phospholipase C; PROPPIN:
β
-‐propeller that bind phosphoinositide species domain; PtdInsP:
Phosphorylated inositol lipids; PTEN: Phosphatase and Tensin Homologue; PX: Phox homology
domain; SHIP: SH2domain-‐containing inositol 5’-‐phosphatase.
2. CLASS I, II, III PI3K, ANDPI3K-‐LIKEKINASES
Of interest to the development and effect of PI3K-‐specific inhibitors, PI3Ks
have sequence similarity with a number of other related serine and threonine
protein kinases collectively known as “PI3K-‐like protein kinases”, or PIKK. These
PIKKplaya role in thecellular response tostresses likeDNAdamageor replication
block, mRNA splicing errors and nutrient deprivation. Importantly, PIKK include
one of the main downstream effectors of class I PI3K activation in lymphocytes,
namely themechanistic target of the immunosuppressant Rapamycin (mTOR), but
also the ataxia-‐telangiectasiamutatedprotein (ATM), the ataxia-‐ andRad3-‐related
protein (ATR), and the DNA-‐dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-‐
PKcs) (6,7). DNA-‐PK is required for the activation of the non-‐homologous end-‐
joiningpathway torepairdouble-‐strandDNAbreaks inducedby ionizing radiation.
Furthermore, DNA-‐PK activates protein kinase B (Akt), another primer target of
class I PI3K, and is particularly important to lymphocyte biology as itsmutation is
a cause for severe combined immunodeficiency (8). Structural homology among
PI3K isoforms, orbetweenPI3KandPIKK(6) has the consequence that frequently,


