JoséMaríaRojo, Pilar Portolés
96
catalytic subunits by small GTPases of theRas family, witha clear selectivityof the
different catalytic subunits foractivationbydistinctRas familymembers (16).
The signaling outcome of PI3K is also controlled by the activity of
PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
phosphatases that are essential to correct lymphocyte function
(17-‐19) (Figure 1, 3). The PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
3-‐phosphatase Phosphatase and Tensin
Homologue (PTEN) controls PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
levels by generating PtdIns(4,5)P
2
;
PTEN is particularly important to control basal levels of PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
. The
PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
5-‐phosphatases SHP-‐1andSHP-‐2 (SH2domain-‐containing Inositol
Phosphatase-‐1 and -‐2) dephosphorylate PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
levels yielding
PtdIns(3,4)P
2
. Interestingly, SHP-‐1, 2 bind to surface molecules of lymphocytes
that are essential tonegatively control immune responses includingCTLA-‐4, PD-‐1,
andBTLA(17).
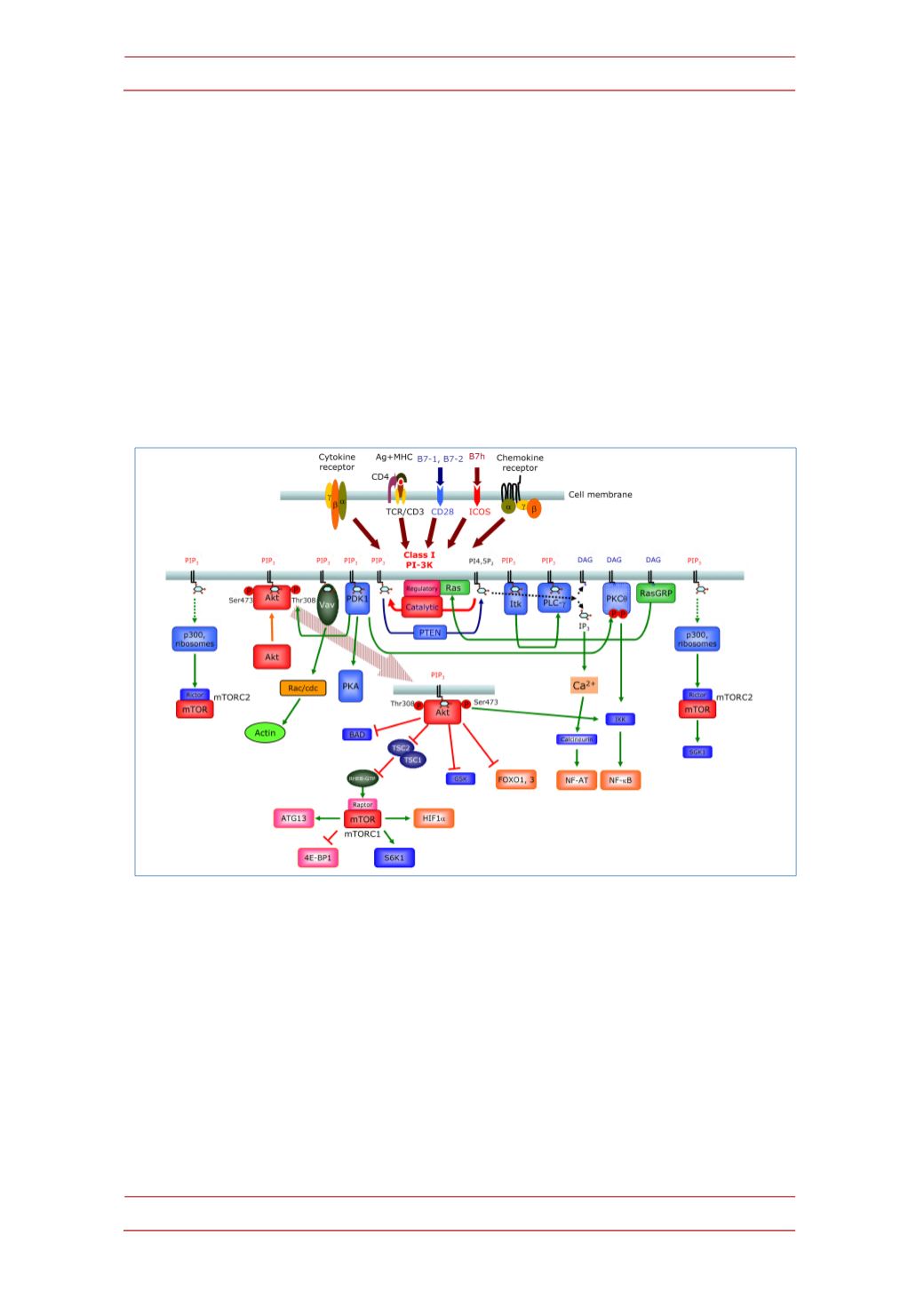
Figure 3.
Adiagramof class I PI3K-‐mediated signaling in T (CD4
+
) lymphocytes. Class IAPI3K are
recruited to the cell membrane and activated upon binding of ligands for cytokine and antigen
receptors or CD28 family costimulator molecules like CD28 or ICOS. Class IB subunits are
characteristically recruited and activated upon binding of chemokines to their G protein-‐coupled
receptors. Enhanced levels of PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
(PIP
3
) favor the recruitment and activation of
proteins containing PH domains including Ser and Thr kinases like PDK1 and Akt, Tec family
protein Tyr kinases (Itk), phospholipases like PLC-‐
γ
, or GEF like Vav. Akt is activated by
phosphorylation of Thr308 and Ser473 by PIP
3
–dependent activated PDK1 and mTORC2,
respectively. Akt has an array of different targets involved in many cell functions. One major
effector of Akt is the mTORC1 complex containing the Ser/Thr kinase mTOR and Raptor. This is
achieved by inactivation/phosphorylation of the tuberous sclerosis 1 and 2 complex (TSC1-‐TSC2)
that blocksRHEB (Ras homologue enriched inbrain), a small GTPase andmTORactivator. Through
phosphorylation of other substrates like ATG13 (autophagy-‐related protein 13), S6K, 4E-‐BP1, or
HIF-‐1
α
, mTORC1 controls important cell processes including autophagy or cell metabolism. Akt
also regulate apoptosis through Bcl-‐2-‐associated death promoter (BAD) protein phosphorylation,
the transcription of genes controled by FOXO transcription factors, or Glycogen synthase kinase
(GSK) 3-‐mediated effects on cell cycle andmetabolism. mTORC2 and PDK1 also phosphorylate the


