730
fibroblast L929 cells. In addition, Yang et al, (42) showed that ajoene exerts
apoptotic activity in 3T3L1 cells by increasing intracellular ROS levels. The results
of the current study demonstrate that curcumin exerts apoptotic effect on 3T3L1
cells in an ROS generation-independent fashion.
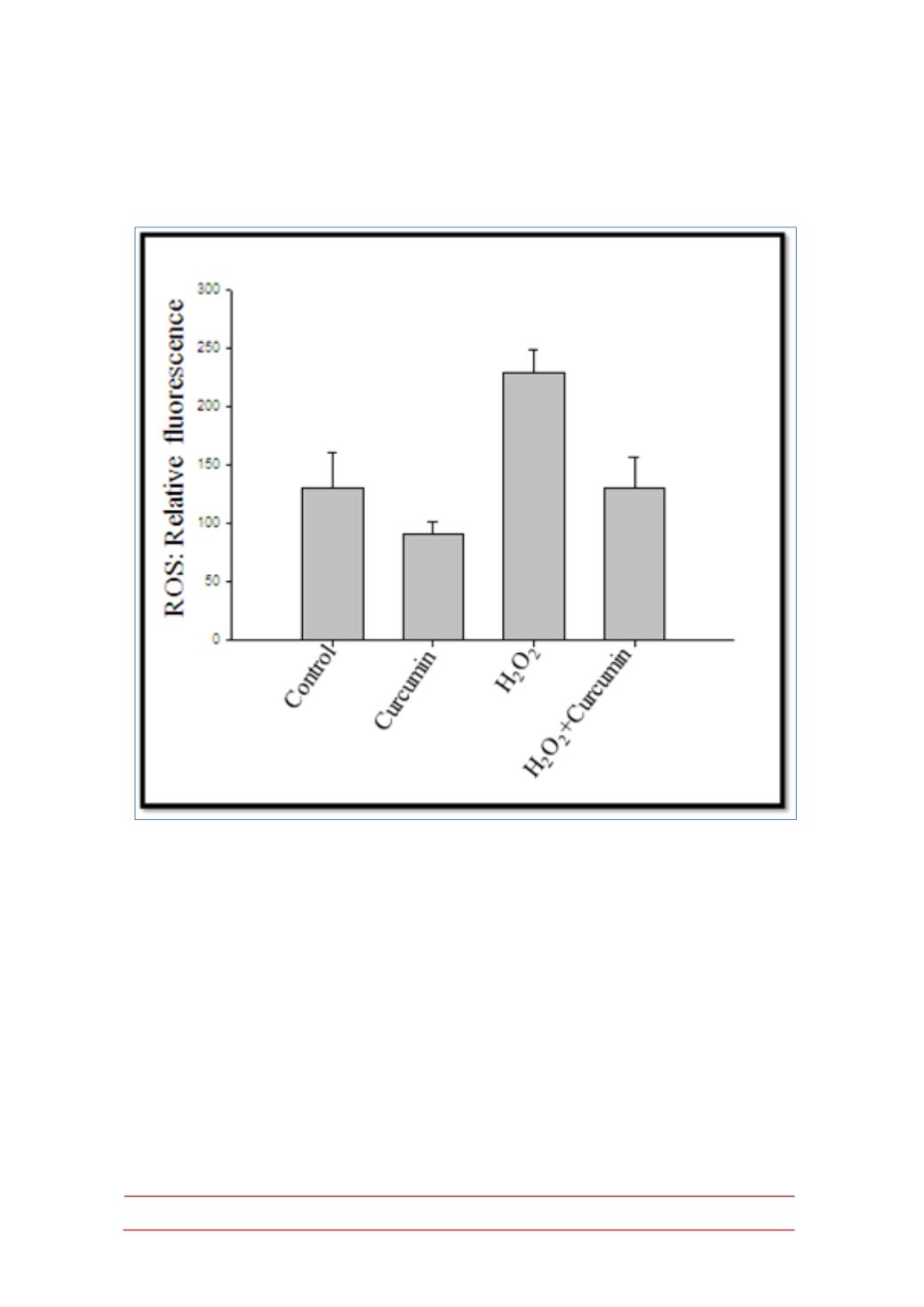
Figure 6.- Showed curcumin (40µM) inhibiting effect on ROS generation level induced with/
without H
2
O
2
in 3T3L1 adipocytes.
Western blot analysis revealed that curcumin inhibited 3T3L1 viability and
affected cellular signalling, including PKA pathway inhibitions, cyclic adenosine
mono phosphate (cAMP) is an essential intracellular second messenger for
controlling a variety of cellular processes, and PKA is its primary target (43). In
this study, 40 µM curcumin increased p-AMPK levels (Figure 4) but inhibited
expression of the PKA catalytic subunit and its relative activity (Figure 5). PKA has
four subunits, and the dissociated active catalytic subunits elicit cellular responses
by increasing the phosphorylation of several proteins. cAMP-mediated
transcriptional responses requires the ability of PKA to phosphorylate CREB (30) .
Induction of CREB is followed by the expression of many transcription factors that
support adipogenesis (13,44,45). To identify the physiological importance of PKA


